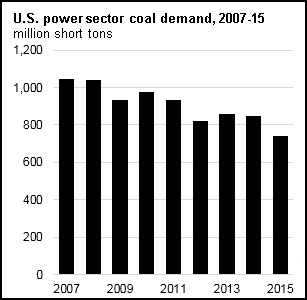
From 2007 to 2015, the use of steam coal for generating electricity has fallen 29% from its top of 1,045 million short tons (MMst) in 2007 to 739 MMst in 2015. Coal use fell in almost every state, rising just in Nebraska and Alaska over that period. States with the biggest decreases were in the Midwest and Southeast, with six states in these locales representing almost 50% of the national decline.
In the United States, 97% of all steam coal is utilized to produce electricity. The cost and accessibility of fuels other than coal, namely natural gas, have majorly affected coal utilization since 2007. An expanded natural gas supply and a subsequent gas cost decline, has resulted in increases in uses of gas for electricity generation, at the expense of coal. This increased availability of low cost natural gas is generally responsible for the lower electricity rates you have seen across most markets. Electricity generation from wind and solar powered sources likewise expanded over this period, driven by tax credits, and innovation in the industry.
With respect to Texas, as the chart below shows, Texas has declined in coal use by 16% from 2007 to 2015.
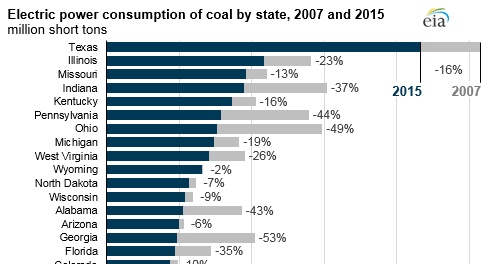
This information here was gathered from the Energy Information Administration. A Division of the U.S. Department of Energy.
To see more on this subject see the article: Power sector coal demand has fallen in nearly every state since 2007